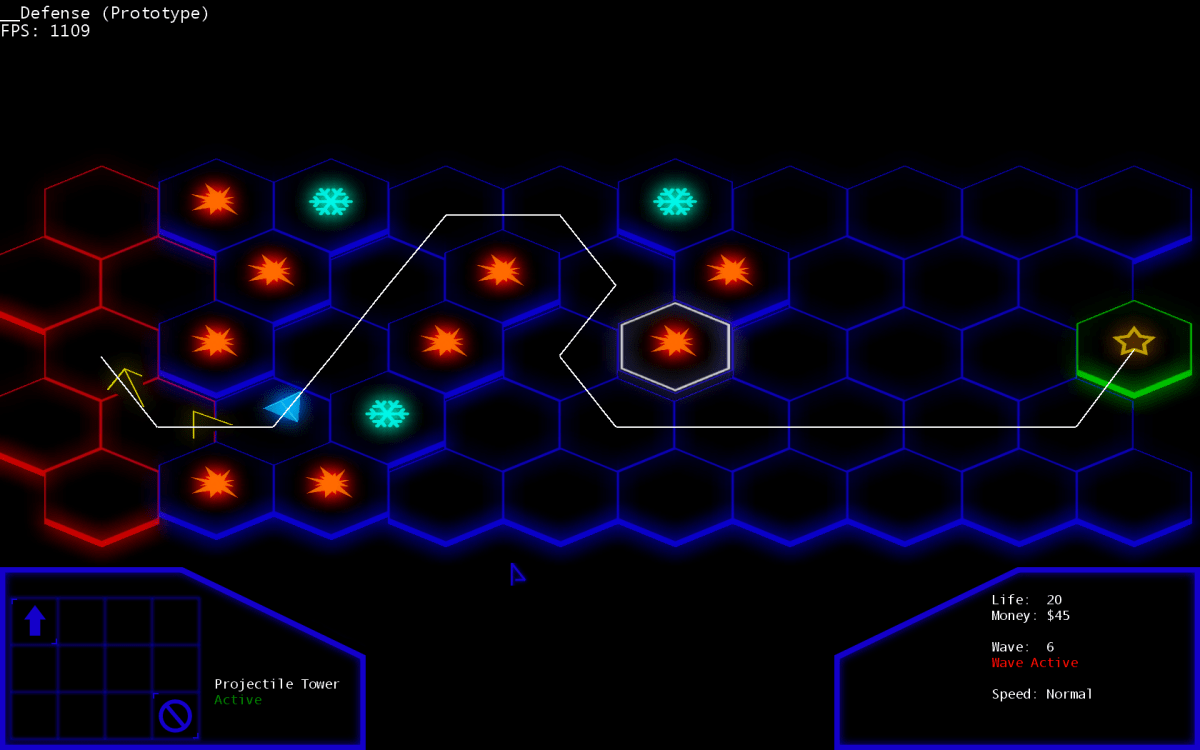
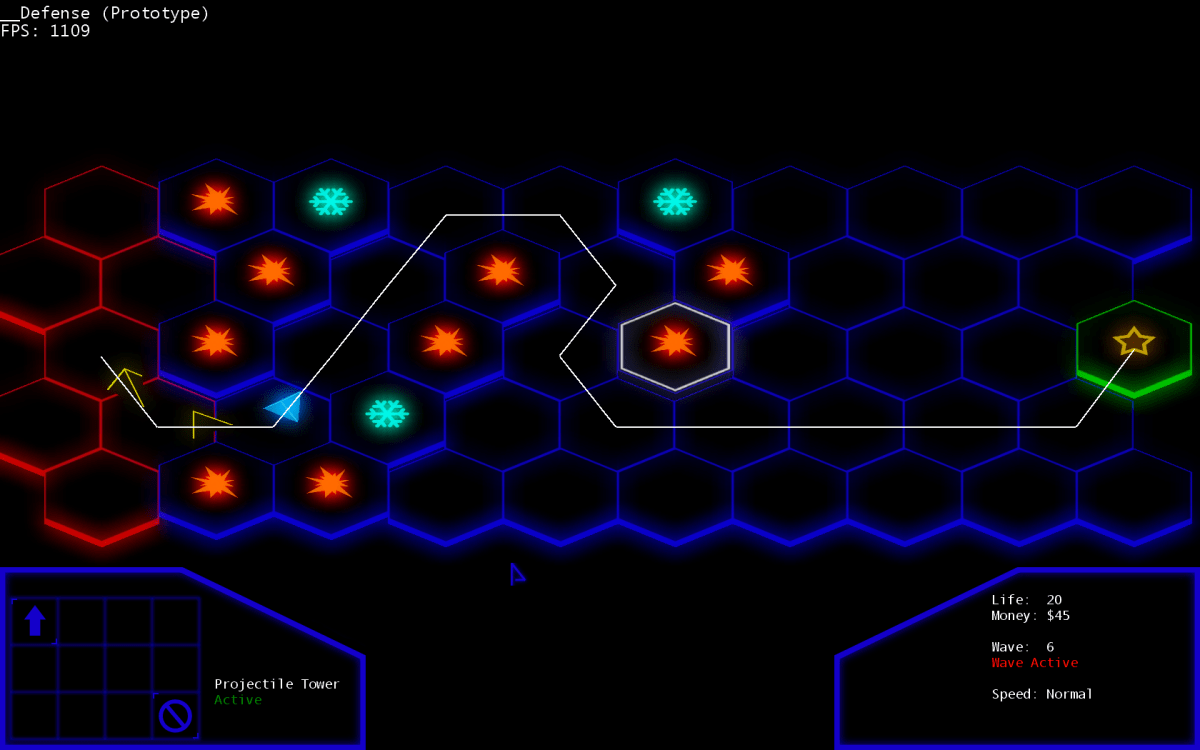
Defender Game: Dive into the captivating world of strategy and defense! We’ll explore the core mechanics, from classic tower defense to innovative subgenres, uncovering the secrets behind engaging gameplay and successful monetization. Get ready to build your own fortress of fun!
This guide covers the fundamental game mechanics, diverse subgenres, crucial design elements, effective monetization strategies, and exciting future trends within the defender game landscape. We’ll examine resource management, enemy AI, level design, visual appeal, and the ethical considerations of in-game purchases. Prepare to learn how to craft a compelling and profitable defender game experience.
Game Mechanics of Defender Games
Defender games, encompassing a broad spectrum of subgenres, share a common thread: protecting something valuable from encroaching enemies. This core gameplay loop is built upon strategic resource management, enemy wave patterns, and the deployment of defensive units or structures. Understanding these mechanics is crucial to appreciating the diverse experiences offered within the genre.
Core Gameplay Loop
The typical defender game loop involves preparing defenses, facing waves of enemies, upgrading defenses, and repeating the cycle with increasing difficulty. Players strategically position defensive units, manage limited resources, and adapt their strategies based on the incoming enemy types and patterns. Successful defense hinges on effective resource allocation, understanding enemy weaknesses, and anticipating upcoming challenges.
Comparison of Tower Defense and Other Subgenres

While tower defense games represent a prominent subgenre, others like base defense and lane defense games offer variations on the core mechanic. Tower defense games primarily focus on stationary towers, whereas base defense games might involve defending a central structure with mobile units or structures. Lane defense games restrict enemy movement to specific paths, simplifying strategic placement but demanding precise timing and resource management.
Resource Management
Resource management is a pivotal aspect of defender games. Players often collect resources over time or earn them by eliminating enemies. Careful allocation of these resources to upgrade existing defenses, construct new ones, or acquire special abilities is key to survival. The scarcity of resources introduces a layer of strategic depth, forcing players to prioritize and make difficult choices under pressure.
Enemy AI and Gameplay Impact
Enemy AI significantly impacts the challenge and replayability of defender games. Simple AI might involve enemies following a fixed path, while more sophisticated AI might include pathfinding, special abilities, and coordinated attacks. Diverse enemy types with varying strengths and weaknesses demand adaptable strategies, preventing monotonous gameplay and fostering strategic thinking.
Hey, want to test your skills and strategy? Defender games are awesome for that! Check out this cool one, the defender game at DroneFair, it’s got some really fun challenges. Seriously, defender games are a great way to unwind and have a blast while sharpening your wits. So go give it a shot!
A New Defender Game Mechanic: Dynamic Terrain Modification
Imagine a defender game mechanic where players can actively modify the terrain to their advantage. For example, they could build walls, create chokepoints, or even trigger environmental hazards to impede enemy progress. This mechanic would add a layer of proactive defense, moving beyond simply placing static defenses and demanding more dynamic tactical choices.
Defender Game Subgenres
The defender genre has branched into numerous subgenres, each offering unique gameplay experiences. These variations often stem from differences in resource management, enemy types, and the overall strategic approach required. Understanding these subgenres helps in appreciating the diversity within the genre.
Subgenre Categorization and Examples
Popular subgenres include Tower Defense (Plants vs. Zombies, Kingdom Rush), Base Defense (StarCraft II, Fortified), and Lane Defense (Plants vs. Zombies 2, Fieldrunners). Each offers a distinct gameplay experience. Tower Defense emphasizes strategic tower placement, Base Defense focuses on defending a central structure, and Lane Defense restricts enemy movement to specific paths.
Evolution of Subgenres
Defender games have evolved significantly. Early titles often featured simple gameplay and limited enemy variety. Modern games incorporate complex AI, diverse unit types, intricate level design, and sophisticated resource management systems. The integration of RPG elements, such as hero upgrades and skill trees, has also become increasingly common.
Comparison of Subgenres, Defender game
| Subgenre | Resource Management | Enemy Types | Gameplay Style |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tower Defense | Often involves collecting gold or mana to build and upgrade towers. | Diverse range of units with unique abilities and weaknesses. | Strategic placement of towers to maximize damage and control enemy flow. |
| Base Defense | Resource gathering and base construction play a significant role. | Multiple enemy types with varying attack patterns and strengths. | Combination of base building, unit deployment, and resource management. |
| Lane Defense | Resource management focuses on upgrading units and deploying new ones along the lanes. | Waves of enemies moving along predetermined paths. | Fast-paced gameplay focused on efficient unit deployment and upgrade timing. |
Game Design Elements in Defender Games
The success of a defender game hinges on more than just compelling gameplay mechanics. Effective level design, engaging visuals, and immersive sound design all contribute to a holistic and enjoyable player experience. These elements work synergistically to create a captivating and replayable game.
Defender games, those classic shoot-’em-ups, are always a blast. Remember how intense they were? It reminds me of the drama surrounding Khabib Nurmagomedov, who was apparently khabib removed from plane , causing a whole other level of unexpected tension. That kind of unexpected event really throws you off, much like a sudden swarm of enemies in a Defender game.
So, next time you play, think about that unexpected twist!
Effective Level Design
Effective level design in defender games involves creating diverse maps with strategic chokepoints, varied terrain, and opportunities for creative defense strategies. Well-designed levels provide a challenge without being frustrating, encouraging experimentation and rewarding skillful play. Consider the classic levels in games like Plants vs. Zombies, known for their challenging yet fair designs.
Visual Appeal and User Interface
A visually appealing and intuitive user interface is crucial for a positive player experience. Clear visual cues, easy-to-understand controls, and a polished aesthetic contribute to a more enjoyable and less frustrating gaming experience. The visuals should also fit the game’s tone and theme, enhancing the overall immersion.
Sound Design and Music
Sound design and music play a vital role in creating atmosphere and enhancing the gameplay experience. Sound effects should provide clear feedback on player actions and enemy behavior. Music should complement the game’s tone, building tension during intense moments and providing a sense of accomplishment during victory.
Essential Elements for a Successful Defender Game
- Engaging gameplay loop
- Strategic depth and replayability
- Well-designed levels with varying difficulty
- Intuitive and visually appealing user interface
- Immersive sound design and music
- Balanced resource management system
- Diverse and challenging enemy AI
Impact of Different Art Styles

- Cartoonish: Creates a lighthearted and accessible atmosphere, suitable for a wide audience.
- Realistic: Can enhance the sense of immersion and stakes, particularly in more serious or strategic games.
- Stylized: Offers a unique visual identity and can appeal to a niche audience with its distinctive aesthetic.
- Pixel Art: Provides a nostalgic feel and can be surprisingly effective in creating charming and engaging visuals.
Monetization Strategies for Defender Games
Monetization strategies significantly impact a defender game’s success and sustainability. The choice of model—free-to-play, premium, or a hybrid approach—requires careful consideration of player expectations, ethical considerations, and the game’s overall design.
Comparison of Monetization Models
Free-to-play models often rely on in-app purchases for cosmetic items, power-ups, or time-saving features. Premium models offer the complete game for a one-time purchase. Hybrid models combine aspects of both, offering a base game with optional in-app purchases. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical monetization practices are crucial. Avoid pay-to-win mechanics that provide unfair advantages to paying players. Transparency in pricing and in-app purchases is also essential. Respecting player time and avoiding aggressive monetization tactics builds trust and fosters a positive player community.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Strategies
Games like Clash of Clans successfully utilize a free-to-play model with optional in-app purchases for cosmetic items and time-saving features. Conversely, games with overly aggressive monetization practices, requiring significant spending to progress, often face negative player reviews and community backlash.
Monetization System Design for a New Defender Game
A new defender game could adopt a hybrid model. The core gameplay would be available for free, with optional purchases for cosmetic tower skins, unique hero units, and a battle pass system offering rewards for completing in-game challenges. This balances accessibility with revenue generation.
Defender games, with their retro charm and addictive gameplay, often make you wonder about the strangest things. For instance, while battling waves of aliens, you might find yourself questioning the plot holes of other shows; check out this article asking the burning question, is thanos alive in squid game , before returning to your high-score chase in your favorite Defender game.
It’s a surprisingly relevant tangent!
Pros and Cons of Monetization Strategies
| Monetization Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Free-to-Play | Wider player base, potential for high revenue | Risk of pay-to-win, potential for negative player perception |
| Premium | Higher perceived value, less player friction | Smaller player base, limited revenue potential |
| Hybrid | Balances accessibility and revenue generation | Requires careful balancing to avoid alienating players |
The Future of Defender Games
The defender game genre shows immense potential for future innovation and growth. Emerging technologies, evolving player expectations, and creative game design will continue to shape its evolution.
Future Trends and Innovations
We can expect to see more sophisticated AI, more dynamic level designs, and the integration of new mechanics that add depth and replayability. The incorporation of procedural generation could lead to near-infinite replayability. Enhanced social features, such as cooperative gameplay and competitive leaderboards, will also become more prominent.
Emerging Technologies and Applications
VR and AR technologies offer exciting possibilities. VR could provide immersive, 360-degree views of the battlefield, enhancing strategic decision-making. AR could overlay defensive structures onto real-world environments, creating unique gameplay experiences.
Predictions for Gameplay Mechanics and Design
We might see the emergence of new subgenres, blending defender mechanics with other genres like roguelikes or puzzle games. More emphasis will be placed on storytelling and character development, transforming the genre beyond its traditional strategic focus.
Conceptual Design for a Futuristic Defender Game
Imagine a defender game set on a space station under attack by alien forces. Players manage robotic defense systems, utilizing energy shields, laser turrets, and drone swarms to repel the invaders. The game would feature dynamic environmental hazards, such as zero-gravity sections and energy surges.
Hypothetical Defender Game with Unique Art Style and Mechanic
Envision a defender game with a vibrant, low-poly art style, set in a whimsical fantasy world. The core mechanic involves controlling elemental spirits to defend a mystical forest. Players summon wind spirits to push enemies back, fire spirits to inflict damage, and water spirits to create defensive barriers. The game would emphasize strategic elemental combinations and environmental interactions.
Conclusive Thoughts
Creating a successful defender game requires a blend of strategic gameplay, compelling design, and thoughtful monetization. By understanding the core mechanics, exploring diverse subgenres, and mastering design elements, you can craft a truly engaging and rewarding experience for players. The future of defender games is bright, filled with innovative possibilities and emerging technologies, ready for you to shape.
FAQ Insights
What makes a defender game successful?
A winning combination of engaging gameplay mechanics, intuitive controls, visually appealing graphics, and a well-balanced monetization strategy are key.
What are some popular examples of defender games?
Popular examples include Plants vs. Zombies, Kingdom Rush, and Bloons TD.
How important is level design in defender games?
Level design is crucial. It dictates the player’s experience and strategic options, influencing challenge and replayability.
What are some emerging trends in defender games?
We’re seeing increased use of VR/AR, more complex AI, and innovative monetization models like battle passes.